Step-by-Step Guide to Puddling in Rice Farming
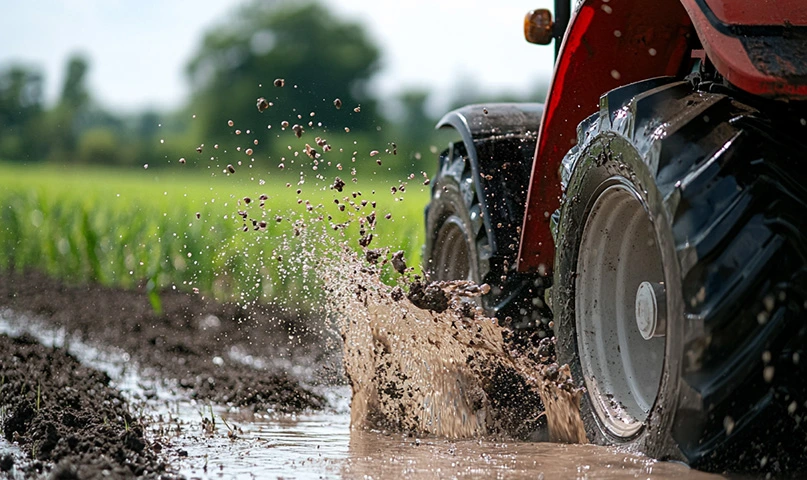

Puddling is a crucial farming practice in rice cultivation, particularly in areas with heavy clay soils or where rice fields are flooded. It involves the deliberate manipulation of soil to create a soft, waterlogged environment that promotes optimal rice growth. The practice helps in weed control, improves soil structure, and prepares the land for the transplantation of rice seedlings. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step guide to puddling in rice farming.
1. Preparation of the field

Before you begin puddling, it's important to prepare the field adequately. Here’s how you can go about it:
- Land leveling: Ensure that the land is leveled for proper water distribution. Uneven land can cause waterlogging in some areas and drought in others, both of which are harmful to rice crops.
- Water management: Rice farming is typically done in flooded fields (known as paddy fields). The field should be flooded with about 4-6 inches of water before starting the puddling process. The water level must be consistent throughout the field to ensure uniform puddling.
- Soil condition: Ideal conditions for puddling are when the soil is moist but not overly saturated. If the soil is too dry, puddling becomes difficult, and if it is too wet, the soil may become too sticky, making it difficult to work with.
2. Use of puddling equipment

There are different ways to puddle a rice field, and the method you use will depend on the available equipment and the size of the field. The most common equipment used for puddling includes:
- Tractors with rotavators: For larger fields, using a tractor-mounted rotavator or rotary tiller is the most efficient method. The rotavator breaks up the soil, mixes it with water, and creates the desired soft, slushy texture that facilitates seedling transplantation.
- Manual labor (traditional method): In smaller fields, farmers may use manual labor with tools like a plough, mattock, or hoe to puddle the soil. Though time-consuming, this method is still common in many rural areas.
- Animal-driven equipment: In some places, especially in regions with traditional farming practices, animals are used to walk through the flooded fields, which helps in compacting and mixing the soil.
3. Puddling process

Once the field is prepared and the right equipment is in place, it’s time to begin puddling. The puddling process typically follows these steps:
a. Breaking the soil surface
If you are using a tractor or a manual tool, begin by breaking up the soil’s surface. The primary goal at this stage is to loosen the soil so that it can absorb more water. The soil should be turned and mixed in a way that it becomes a slurry, which will help in rice transplanting. The water should remain mixed with the soil during this process, but it should not be too deep.
b. Mixing water and soil thoroughly
As you continue puddling, ensure that the soil is thoroughly mixed with water. This will result in a slurry-like consistency that is essential for rice seedling roots to grow and establish a strong foundation. The soil should be fine enough to prevent clogging of the transplanting machine or hinder seedling root penetration.
c. Compaction of soil
The next step is to compact the soil. Compaction ensures that the rice plants are able to grow in a firm foundation. It also helps in minimizing the chance of water loss through seepage. This can be achieved through the movement of tractors or animals that walk through the waterlogged field.
d. Leveling the field once again
After puddling, it’s essential to check the field for any uneven areas. Leveling the field ensures that the water remains uniformly distributed. This can be done manually with a simple tool like a leveling board or through more advanced machinery.
e. Maintaining water level
Once the field is puddled and leveled, maintain a consistent water level of around 4-6 inches. This will prevent soil erosion and help with the establishment of seedlings. Make sure the water remains stagnant during the initial stages after puddling to keep the soil submerged.
4. Weed control

Puddling is not only beneficial for soil structure but also for controlling weeds. By mixing the soil and water, many weed seeds are either drowned or uprooted, reducing the need for herbicides. However, some weeds may still grow, so farmers may need to use manual labor or herbicide application after puddling to ensure minimal competition for nutrients.
5. Transplanting rice seedlings

After puddling, the field is ready for transplanting rice seedlings. This process typically involves transplanting young rice plants (nursery-grown seedlings) into the puddled soil, where they will take root and grow into mature rice plants.
- Transplanting method: You can use manual labor to transplant the seedlings or use a machine, depending on the size of the field and available resources.
- Spacing: Proper spacing between rice plants is crucial for optimal growth. Generally, rice plants are spaced about 6–8 inches apart in rows to allow them ample space for growth and water absorption.
6. Post-puddling field care

Once the rice seedlings are transplanted, you’ll need to take care of the field for the duration of the growing season. Here are some post-puddling tasks to keep in mind:
- Water management: Ensure the field remains flooded to an optimal depth, especially during the early stages of growth. Adjust the water level to avoid drought stress or waterlogging.
- Fertilization: Use appropriate fertilizers based on soil and plant needs. Typically, nitrogen-rich fertilizers are used during the early stages of rice growth.
- Weed and pest management: Even though puddling helps in weed control, some weeds and pests may still arise. Regularly inspect the field and apply herbicides or pesticides as necessary.
- Monitoring soil health: Keep an eye on the soil’s health throughout the growing season. Ensure that the soil remains compact enough for rice growth without becoming too waterlogged.
7. Harvesting

After the rice has matured, it’s time for harvesting. Typically, rice is harvested once the grains have ripened, and the stalks turn yellow. Proper harvesting methods ensure that the grains are preserved without damage.
Conclusion
Puddling is a vital technique in rice farming that significantly impacts the growth and yield of the crop. By following this step-by-step guide, you can master the art of puddling and create an optimal environment for rice cultivation. Remember that careful preparation, consistent water management, and diligent post-transplant care are key to a successful rice harvest. Happy farming!