Kisan Credit Card Scheme: Guide to Eligibility, Application and Benefits

The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme is one of the most significant financial initiatives by the Government of India to empower farmers. Introduced in August 1998, the scheme was designed by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) on the recommendations of the R. V. Gupta Committee. Since then, it has become a vital instrument to provide affordable, timely, and flexible credit to farmers across the country.
Over the years, the KCC scheme has undergone several improvements. Initially aimed at providing short-term credit for crop production, it was later extended in 2004 to cover investment credit for allied and non-farm activities. In 2012, the scheme was further revised under the chairmanship of Shri T. M. Bhasin to simplify the procedures and enable the issue of electronic Kisan Credit Cards (e-KCC).
With the introduction of technology-driven banking, integration with Aadhaar authentication, RuPay cards, and mobile banking, the KCC has evolved into a comprehensive tool to meet the diverse credit needs of the Indian farmer.
Objectives of the Kisan Credit Card Scheme
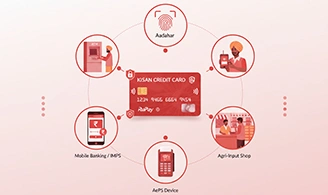
The primary objective of the Kisan Credit Card scheme is to provide farmers with adequate and timely credit support for agriculture and related activities under a single window. The scheme is designed with flexible procedures to make credit accessible and hassle-free.
Key Purposes of KCC:
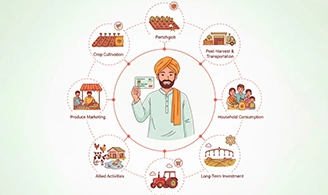
- To meet short-term credit requirements for crop cultivation.
- To cover post-harvest expenses, including storage and transportation.
- To provide produce marketing loans.
- To support household consumption needs of farming families.
- To ensure working capital for maintenance of farm assets and allied activities like dairy, poultry, or fisheries.
- To extend investment credit for long-term agricultural development such as land improvement, irrigation, or purchase of equipment like tractors.
By catering to these needs, the KCC scheme ensures that farmers do not have to depend on informal moneylenders charging high interest, thereby reducing financial stress in rural households.
Key Features of the Kisan Credit Card

The KCC scheme has evolved into a modern financial product equipped with smart banking features.
- Type of Card
- Magnetic stripe card with PIN for ATM access.
- Biometric authentication using Aadhaar or UIDAI infrastructure.
- EMV or RuPay chip-enabled smart cards for secure transactions.
- Cards are interoperable across banks, ATMs, PoS machines, and input dealers.
- Delivery Channels
- Withdrawals through ATMs or micro-ATMs.
- Transactions through Business Correspondents (BCs) using smart cards.
- Purchases via PoS machines at input dealers.
- Mobile banking with IMPS and IVR support.
- Aadhaar-enabled transactions for seamless rural banking.
These features make the KCC more than just a credit card—it is a financial inclusion tool helping farmers access the banking ecosystem conveniently.
Eligibility for Kisan Credit Card

The KCC scheme covers a wide spectrum of rural borrowers. The eligibility criteria are:
- Individual Farmers – Owner cultivators with landholding.
- Joint Borrowers – Families engaged in farming activities.
- Tenant Farmers – Those cultivating on leased land.
- Oral Lessees and Sharecroppers – Farmers who do not own land but cultivate on a sharing basis.
- Groups of Farmers – Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) including tenant farmers and sharecroppers.
By including small and marginal farmers, as well as tenant cultivators, the scheme ensures inclusive credit access.
Application Process for Kisan Credit Card

Farmers can apply for KCC either online or offline depending on their preference and banking access.
- Online Application
- Visit the official website of the bank (e.g., SBI, PNB, Bank of Baroda).
- Select the Kisan Credit Card option.
- Fill in the application form with details like personal information, landholding, and cropping pattern.
- Submit the form online.
- A reference number is generated, and the bank reviews the application within 3–4 working days.
- Offline Application
- Farmers can visit the nearest branch of their bank.
- Collect the KCC application form or download it from the bank’s website.
- Submit the form along with necessary documents such as land records, ID proof, and photographs.
- The bank verifies the details and processes the application.
Documents Required for Kisan Credit Card

Farmers need to submit the following documents while applying:
- Duly filled Application Form.
- Two passport-size photographs.
- Identity Proof – Aadhaar Card, Voter ID, Driving License, or Passport.
- Address Proof – Aadhaar Card, Driving License, etc.
- Proof of Landholding certified by revenue authorities.
- Cropping pattern details (crops grown and acreage).
- Security documents (for loan amounts above ₹1.6 lakhs/₹3 lakhs, as per bank policy).
- Any other document required by the bank.
Fixation of Credit Limit

One of the most important aspects of the KCC scheme is the credit limit determination, which is done based on the farmer’s cultivation pattern, landholding, and financial needs.
- For Single Crop Farmers (First Year):
- Scale of finance for the crop × Area cultivated.
- +10% towards post-harvest and household expenses.
- +20% towards repair and maintenance of farm assets.
- Crop insurance, PAIS & asset insurance costs.
- For Subsequent Years:
- The first-year limit + 10% increment per year for cost escalation.
- For Multiple Crop Farmers:
- Limit fixed as per proposed cropping pattern.
- 10% increment every year for cost escalation.
- Term Loans:
- For long-term investments such as land development, irrigation, purchase of farm equipment like tractors, or allied activities.
- Maximum Permissible Limit (MPL):
- Short-term limit (5th year) + estimated long-term loan requirement.
- Sub-Limits:
- Separate sub-limits are created for short-term loans and term loans due to differences in interest rates and repayment schedules.
This structured approach ensures that farmers get adequate financial support to manage both seasonal and long-term agricultural needs.
Interest Rates and Subsidies
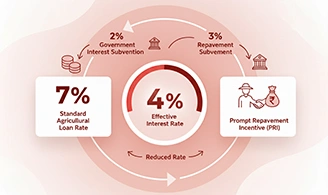
The KCC scheme offers farmers highly subsidized interest rates.
- The standard rate of interest on agricultural loans is around 7% per annum.
- The Government of India provides 2% interest subvention.
- Farmers who make timely repayments are eligible for an additional 3% Prompt Repayment Incentive (PRI).
- Thus, the effective interest rate for farmers is just 4% per annum.
This makes the KCC one of the cheapest credit options available in India compared to informal sources of borrowing.
Benefits of the Kisan Credit Card

The KCC scheme offers a wide range of benefits that go beyond just access to credit:
- Easy Access to Credit – Simplified process and flexible repayment.
- Multiple Uses – Funds can be used for crop production, post-harvest needs, consumption, marketing, and allied activities.
- Low-Interest Rates – With subsidies and incentives, farmers enjoy loans at just 4% interest.
- Insurance Coverage – Crops are covered under schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), along with PAIS and asset insurance.
- Convenience of Transactions – KCC cards work at ATMs, PoS machines, and mobile banking platforms.
- Long-Term Support – Credit for land development, irrigation, and farm mechanization.
- Reduced Dependency on Moneylenders – Farmers get institutional credit at affordable rates, reducing exploitation.
- Financial Inclusion – Even tenant farmers, oral lessees, and SHGs can benefit.
- Flexible Withdrawals – Credit can be withdrawn as per seasonal requirements.
- Boost to Rural Economy – Enhanced liquidity in farmers’ hands increases rural demand and strengthens the overall agricultural ecosystem.
KCC and Tractor Financing

One of the major uses of the Kisan Credit Card limit is for purchase of farm equipment such as tractors, power tillers, and irrigation systems. Tractors have become essential for medium and large-scale farming, and through KCC’s term loan facility, farmers can get easy financing at low interest.
This not only improves farm productivity but also reduces dependence on manual labor, allowing farmers to expand cultivation and adopt modern farming practices.
Challenges in Implementation
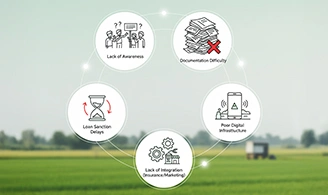
While the KCC scheme has transformed rural credit access, certain challenges remain:
- Lack of awareness among small and marginal farmers.
- Complicated documentation in some cases.
- Delays in loan sanction and card issuance.
- Limited penetration of digital and Aadhaar-enabled infrastructure in remote areas.
- Need for better integration with insurance and marketing systems.
Recent Developments in KCC Scheme
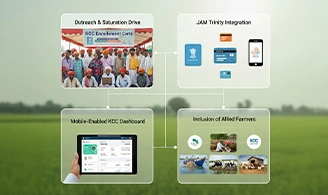
The Government has been making constant efforts to expand the reach of KCC:
- Special KCC saturation drives have been launched to bring all farmers under the scheme.
- Integration with Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) trinity for direct benefit transfers.
- Digitization and mobile-enabled services for real-time monitoring.
- Focus on covering fishermen and livestock farmers under the scheme.
These steps are expected to further strengthen KCC as a comprehensive financial inclusion tool.
Conclusion

The Kisan Credit Card scheme is not just a credit facility—it is a lifeline for millions of Indian farmers. By providing timely, affordable, and flexible credit, it empowers farmers to manage their cultivation, household, and investment needs without falling into the trap of moneylenders.
With features like low interest rates, insurance coverage, integration with modern banking infrastructure, and support for tractor and equipment financing, the scheme plays a crucial role in enhancing agricultural productivity and ensuring financial security for rural households.
However, greater awareness, simplified procedures, and wider digital penetration are essential to maximize its impact. As India continues to modernize its agriculture sector, the KCC scheme remains a cornerstone of rural credit policy, ensuring that farmers—the backbone of our nation—remain financially strong and resilient.
















